Exploring Binary Tree
Binary tree is one of the most fundamental and important data structures in computer science. In this article, we will explore the concept, types, properties, representation methods, and applications of binary trees.
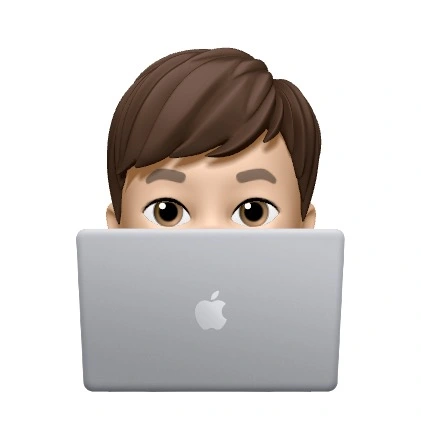
What is a Binary Tree?
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two child nodes. This structure allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and management of data.
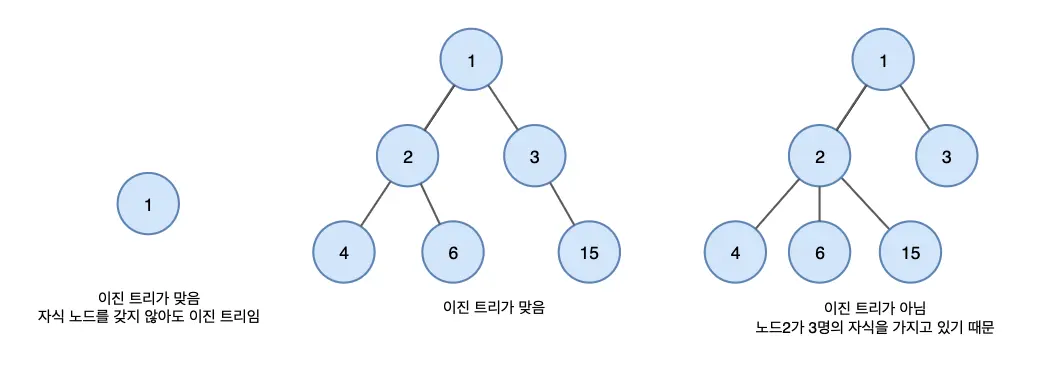
Types of Binary Tree
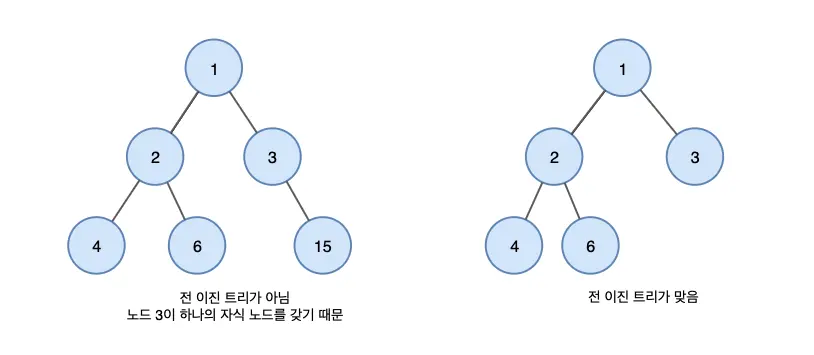
1. Full Binary Tree (Strict Binary Tree)
A full binary tree is a tree in which every node has either 0 or 2 child nodes. In other words, each node must have either no children or exactly two children.
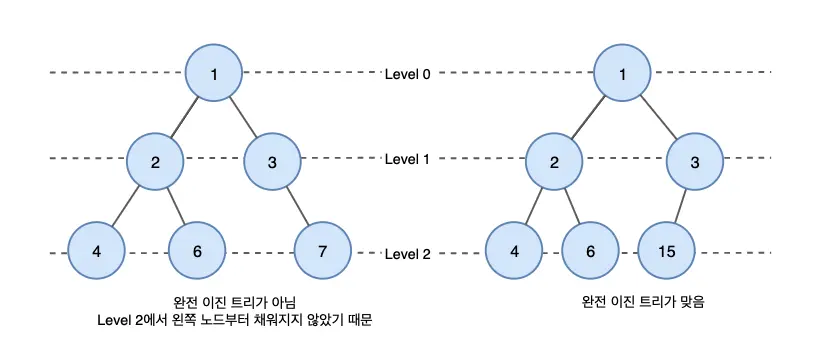
2. Complete Binary Tree
A complete binary tree is a tree where all levels are completely filled except possibly the last level, which is filled from left to right.
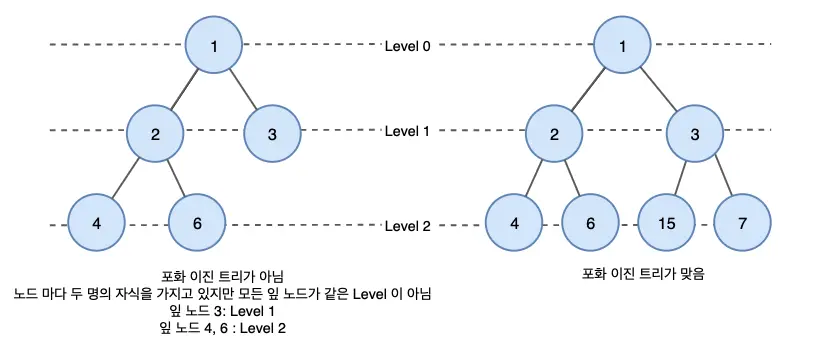
3. Perfect Binary Tree
A perfect binary tree is a tree where all internal nodes have exactly two child nodes, and all leaf nodes are at the same depth or level.
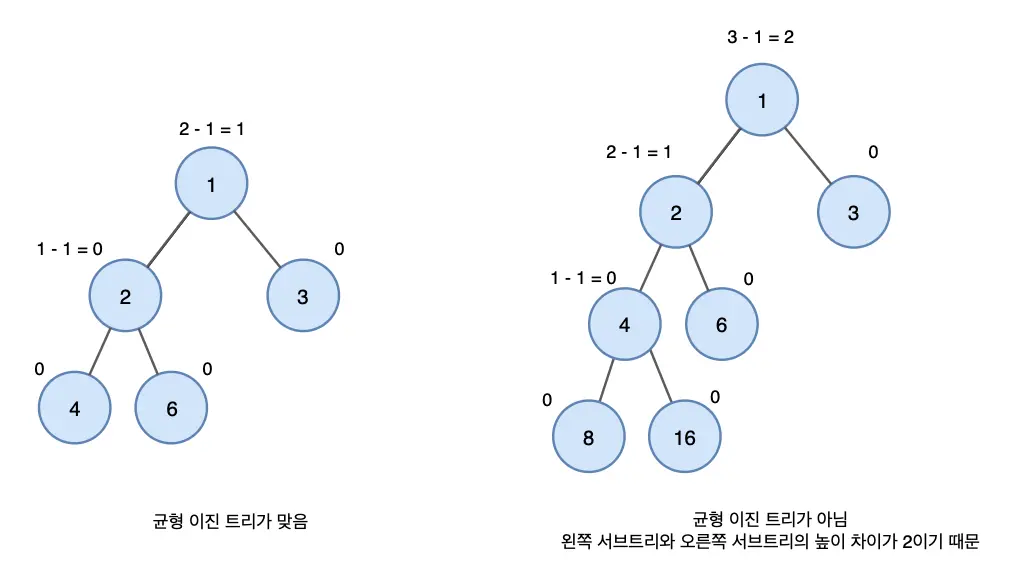
4. Balanced Binary Tree
A balanced binary tree is a tree where the height difference between the left and right subtrees of any node is at most one. AVL trees and Red-Black trees are classic examples.
Properties of Binary Trees
Binary trees have the following properties:
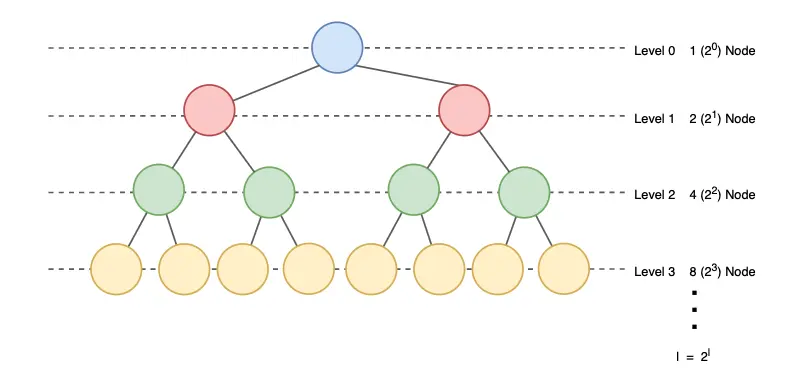
1. The maximum number of nodes at level l of a binary tree is \(2^l\).
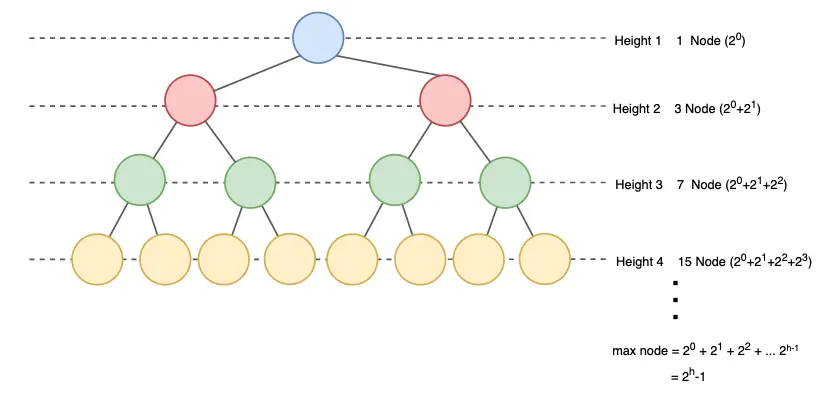
2. For a tree of height h, if the height of a tree with a single node is considered as 1, the maximum number of nodes is \(2^h - 1\). If the height of a single-node tree is 0, then the maximum number of nodes is \(2^{h+1} - 1\).
3. If the height of leaf nodes is 1, the minimum height is \(log_2(N+1)\). If the height of leaf nodes is 0, the minimum height is \(log_2(N+1) - 1\).
\(2^h - 1 = n\)
\(2^h = n + 1\)
\(log_2(2^h) = log_2(n + 1)\)
\(h = log_2(n + 1)\)
4. In a full binary tree, the number of leaf nodes is always one more than the number of internal nodes with two children.
L = number of leaf nodes
T = number of internal nodes with two children
L = T + 1
Representation Methods of Binary Trees
Binary trees can be implemented using arrays or linked lists.
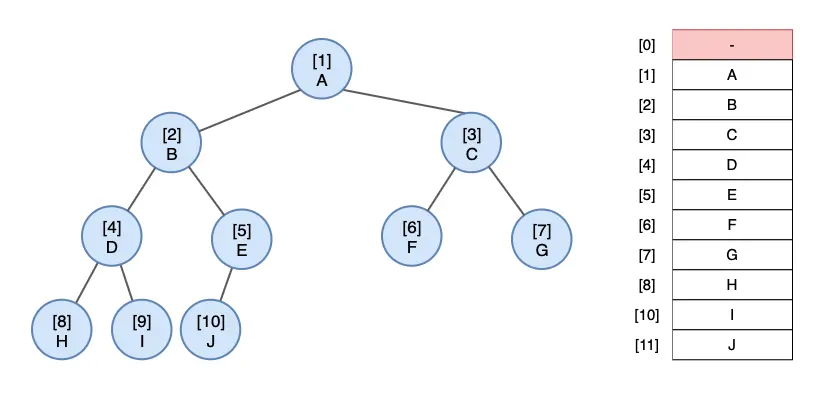
1. Array (Sequential) Representation
Using arrays to represent binary trees allows for easy determination of parent and child relationships based on node indices.
When the root node’s index i is 0:
- The left child of node i is at position 2*i + 1.
- The right child of node i is at position 2*i + 2.
- The parent of node i is at position (i - 1)/2.
When the root node’s index i is 1:
- The left child of node i is at position 2*i.
- The right child of node i is at position 2*i + 1.
- The parent of node i is at position i/2.
Complete Binary Tree Represented in an Array - Efficient Use of Array Space
Skew Tree Representation - Wasting a Lot of Space
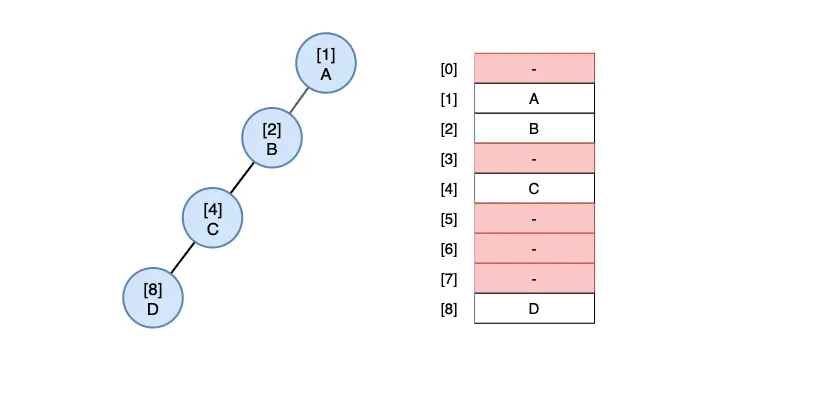
Advantages and Disadvantages of Array Representation
- Advantages: Fast node access and simple implementation.
- Disadvantages: Memory wastage occurs in skewed trees, and there is a limitation on adding nodes beyond the array size.
2. Linked List Representation
By using pointers, each node points to its child nodes, implementing the tree in a linked list form.
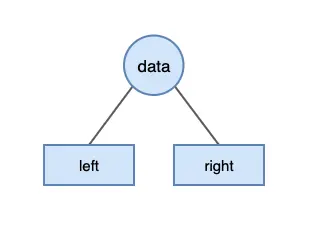
In C language, a binary tree node storing integers can be defined as follows:
struct BinaryTreeNode {
int data;
struct BinaryTreeNode *left;
struct BinaryTreeNode *right;
};
Advantages and Disadvantages of Linked List Representation
- Advantages: No limitation on the number of nodes; easy insertion and deletion.
- Disadvantages: Slower node access compared to arrays.
Applications of Binary Trees
Binary trees play a crucial role in various fields.
- Expression Tree: Represents mathematical expressions in a tree structure to define the order of operations.
- Huffman Coding Tree: Generates an optimal binary tree based on character frequencies in data compression algorithms.
- Binary Search Tree (BST): A tree structure that supports efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations.
- Priority Queue: Uses heap data structures to manage elements based on priority.
