Tree Traversal: Pre-order, In-order, Post-order, and Level-order Traversals
Tree traversal is a method of visiting nodes in a specific order, and each method can be applied to solve various problems. In this article, we will explore the four tree traversal methods: Pre-order Traversal, In-order Traversal, Post-order Traversal, and Level-order Traversal.
What is Tree Traversal?
Tree Traversal refers to the process of systematically visiting every node in a tree structure exactly once. This is fundamental in various operations like processing the tree’s data or finding nodes that meet specific conditions.
The main purposes of tree traversal are:
- Data Processing: Reading or modifying the data of each node.
- Searching: Finding specific values or exploring nodes that meet certain conditions.
- Copying and Transforming: Duplicating the tree or converting it into another structure.
The methods of tree traversal are:
- Pre-order Traversal
- In-order Traversal
- Post-order Traversal
- Level-order Traversal
1. Pre-order Traversal
Pre-order traversal visits the root node first, then the left child, and finally the right child. This method is useful for outputting the structure of the tree or duplicating it.
Order of Pre-order Traversal:
- Visit the root node.
- Perform pre-order traversal on the left subtree.
- Perform pre-order traversal on the right subtree.
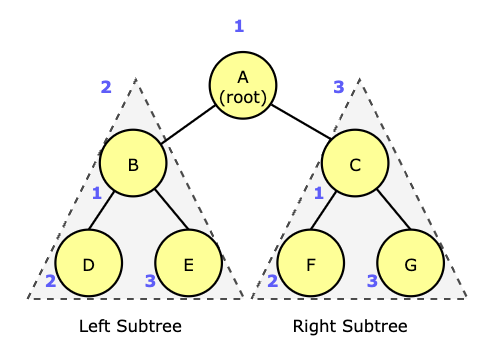
In the diagram above, the result of pre-order traversal is A, B, D, E, C, F, G.
Pre-order Traversal Algorithm (Recursive):
def pre_order(node):
if node:
print(node.value, end=' ') # Visit root
pre_order(node.left) # Visit left subtree
pre_order(node.right) # Visit right subtree
Characteristics of Pre-order Traversal:
- Since the root is visited first, it’s useful for duplicating the tree structure or converting expressions to prefix notation.
- Commonly used when exploring directory structures in file systems.
2. In-order Traversal
In-order traversal visits the left child first, then the root node, and finally the right child. This method plays a crucial role in binary search trees, allowing nodes to be sorted in ascending order.
Order of In-order Traversal:
- Perform in-order traversal on the left subtree.
- Visit the root node.
- Perform in-order traversal on the right subtree.
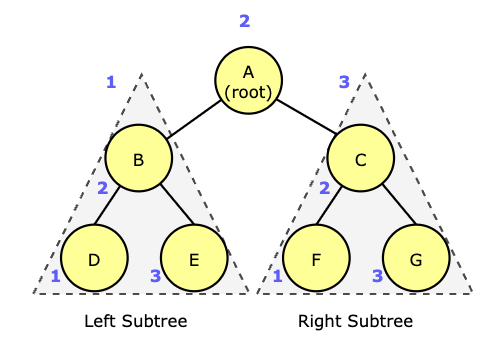
In the diagram above, the result of in-order traversal is D, B, E, A, F, C, G.
In-order Traversal Algorithm (Recursive):
def in_order(node):
if node:
in_order(node.left) # Visit left subtree
print(node.value, end=' ') # Visit root
in_order(node.right) # Visit right subtree
Characteristics of In-order Traversal:
- In a binary search tree, in-order traversal outputs values in sorted order.
- Often used when you need to output the tree structure in order or obtain sorted data.
3. Post-order Traversal
Post-order traversal visits both the left child and right child first, and then the root node last. This method is useful when you need to process all child nodes before the parent node.
Order of Post-order Traversal:
- Perform post-order traversal on the left subtree.
- Perform post-order traversal on the right subtree.
- Visit the root node.
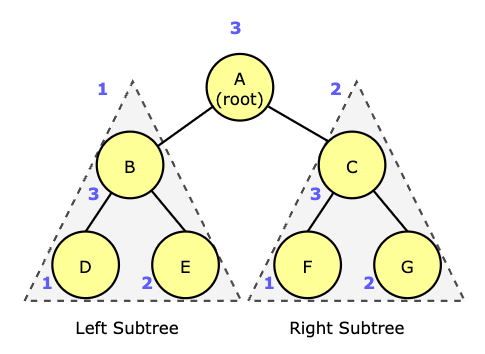
In the diagram above, the result of post-order traversal is D, E, B, F, G, C, A.
Post-order Traversal Algorithm (Recursive):
def post_order(node):
if node:
post_order(node.left) # Visit left subtree
post_order(node.right) # Visit right subtree
print(node.value, end=' ') # Visit root
Characteristics of Post-order Traversal:
- Since child nodes are processed before the parent node, it’s suitable for tasks like deleting tree structures or memory deallocation.
- Often used when deleting directory structures in computer systems.
4. Level-order Traversal
Level-order traversal visits nodes by their level in the tree, starting from the root node at the highest level and moving down one level at a time. This method is implemented using Breadth-First Search (BFS).
Order of Level-order Traversal:
- Visit the root node.
- Visit the nodes at the next level from left to right.
- Repeat this process for all levels.
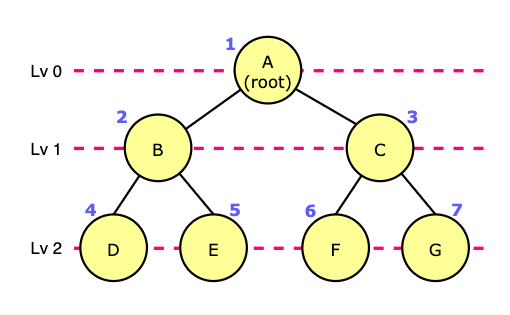
In the diagram above, the result of level-order traversal is A, B, C, D, E, F, G.
Level-order Traversal Algorithm (Using a Queue):
from collections import deque
def level_order(node):
if not node:
return
queue = deque([node])
while queue:
current = queue.popleft()
print(current.value, end=' ')
if current.left:
queue.append(current.left)
if current.right:
queue.append(current.right)
Characteristics of Level-order Traversal:
- Since it visits nodes based on the tree’s height, it’s suitable for problems like finding the shortest path.
- Used in data structures like binary heaps and is useful when nodes need to be processed based on their width.
Comparison of Tree Traversal Methods
| Traversal Method | Order | Characteristics | Main Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-order | Root → Left Child → Right Child | Visits the root node first | Copying tree structures, recursive problem solving |
| In-order | Left Child → Root → Right Child | Visits nodes in sorted order in BST | Sorting values in a binary search tree |
| Post-order | Left Child → Right Child → Root | Processes child nodes before parent nodes | Tree deletion, memory deallocation |
| Level-order | Visits nodes from left to right by level | Breadth-First Search, implemented using a queue | Shortest path search, width-based search |
Conclusion
Tree traversal is an important method for visiting each node in a tree data structure. Each traversal method has advantageous properties in certain situations, so it’s crucial to choose the appropriate traversal method based on the problem’s characteristics and the desired solution approach. By clearly understanding and utilizing the concepts of pre-order, in-order, post-order, and level-order traversals, you can efficiently solve a variety of tree-based problems.
